The basic idea of the PID control system is to figure out how to generate the appropriate actuating signal which is the input, so that the system will produce the desired controlled variable which is the output. This control system is here to help the object to achieve the set point or the desired value. The PID control uses a feedback control which the output of the system is fed back to the input and is compared to the command to see how far away the object is from the target. This difference between the current stage and the set point is the error term. If the output is exactly what we want it to be, then the error would be zero, this is what we are trying to achieve.
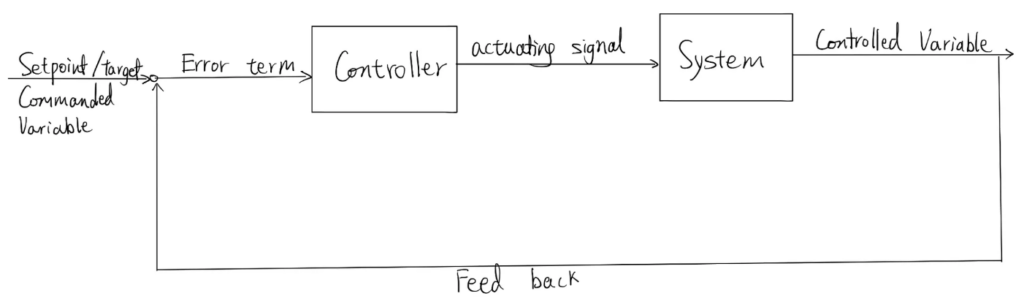
The diagram illustrates the basic idea of how this control is achieved. The system would continuously check for the error term which means how far away is it from the target. According to this error term, an suitable actuating signal would be generated so that the error term would decrease and eventually goes to zero.
Proportional Control
Proportional control is a process control technology that responses in proportion to the difference between the set point(SP) value and current value which is called the error. The resulting error is multiplied with a multiplication factor to get the output. The multiplication factor is called the Proportional Gain Factor (KP)of the proportional controller.
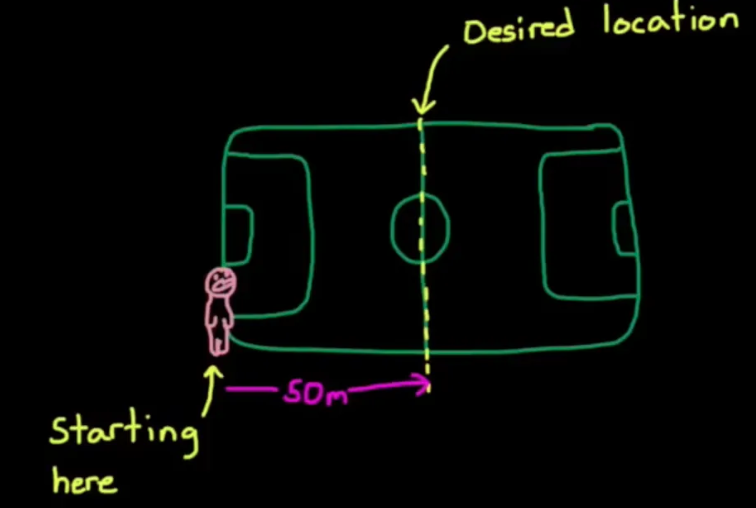
For example, the person above wanted to go to the mid field 50 meters away. At the beginning, his brain notice that there is still a long distance to go, so he is going to run in a fast speed. As he is getting close and closer to the desired location, he would realise that he should decelerate so that he will not exceed this target and stop right on it. In this case, our brain will use the present error to decide the speed. The key objective for the proportional control is to give a large amount of power when there is a long way to go, but only a small amount of power when it is nearly at the set point.
The limitations of proportional control:
- The Proportional Controller produces steady state error. The special term used for this is the offset. This means that after some time, there will be a constant error between the input signal and the output signal. Proportional Controller cannot eliminate this error.
- Proportional controllers also causes overshoots and undershoots in the system.
Integral Control
To solve the steady state error which the proportional control couldn’t eliminate, we can use the integrator. An integrator sums up the input signal over time, it basically keeps track of the past. If a system gets to the steady state below the set point, the error term would be non-zero. When this non-zero error is integrated the output will increase. As long as the system doesn’t reach the target, this integral term would continue to change. This increased value for the integrator will increase the power of the system so that the system will continue to get closer to the target.
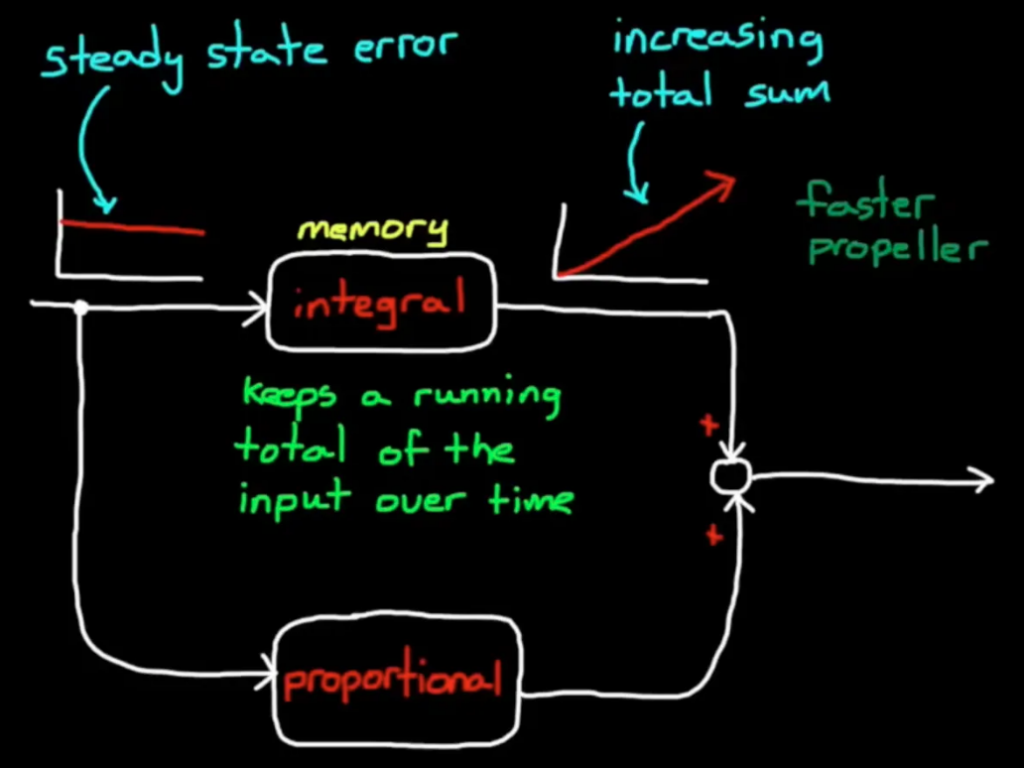
This integral control will work together with the proportional control to allow the system to get to the desired set point. The problem is that sometimes the integral term gets too large and causes an overshoot, meaning that the system goes beyond the desired set point and need a negative error to return.
Derivative Control
To solve the problem of the overshoot, we would need a derivative control. The derivative control will look at the “future” which is the rate of change of the error or in other words how fast the system is approaching the set point. For example, when the system is reaching the set point quickly, the error is quickly decrease. This gives an negative rate of change, thus producing a negative value on the derivative path. This negative value would be added to the output and therefore lowing the speed to prevent overshoot.
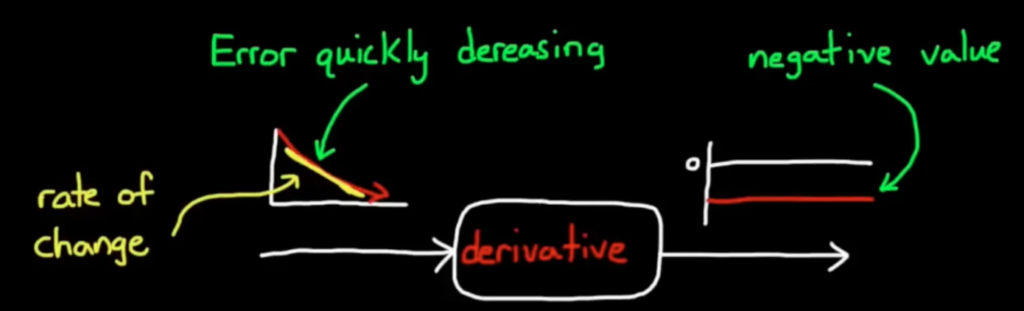
This control basically determines whether or not the system is achieving the target too fast, and by prematurely slowing down the system to avoid overshoot.