What is BCI? (Brain computer interface)
Interface → communication pathway
BCI → The system that provides a communication pathway to convert brain activity signals to instructions recognisable to computers.
Process of basic BCI systems:
- signal acquisition (信号采集)
- Preprocessing: filtering, removing noise and artefacts
- Feature extraction: μ and β rhythm
- Classification: decoding the intention using machine learning algorithm
- Output: control of peripheral device
Characteristics of EEG:
EEG signals originate from the potential changes caused by the discharge of neuron populations and are measured by scalp surface electrodes.
Pros:
- Non-invasive → Safe
- Excellent Temporal Resolution → track brain activity in real time
Cons:
- Signal contains lots of noise.
- Poor spatial resolution → hard to locate the exact position of activity inside the brain
Moter Imagery BCI
It is a mental process of imagining movement in the brain, and it is not accompanied by actual muscle movement
It is reflected in the change in the μ and β rhythm
μ and β signals are obtained from C3, C4 electrode in the electrode cap
μ Rhythm
- 8-13Hz
- Main signal for movement and imagination
- Its ERD often mark the start of imagination (more significant power reduction at the start of the imagination)
β Rhythm
- 13-30Hz
- Main signal for post-movement resetting
- Its ERS often mark the end of motion imagination (more significant power increase at the end of the imagination)
| Feature | Motor Command (Beta Rhythm) | Sensory Feedback (Mu Rhythm) |
|---|---|---|
| Direction | Outgoing (Brain → Body) | Incoming (Body → Brain) |
| Primary Role | To DO – Execute the movement | To FEEL & CHECK – Monitor the result |
| Example | Motor cortex generate signal to raise right hand, this is reflected in the ERD of beta rhythm | Its ERD reflect the sensory areas in the brain are actively engaged in simulating the felt experience of an action, even when no movement occurs. |
Important Concept: The rhythms are a reflection, not the carrier, of the information.
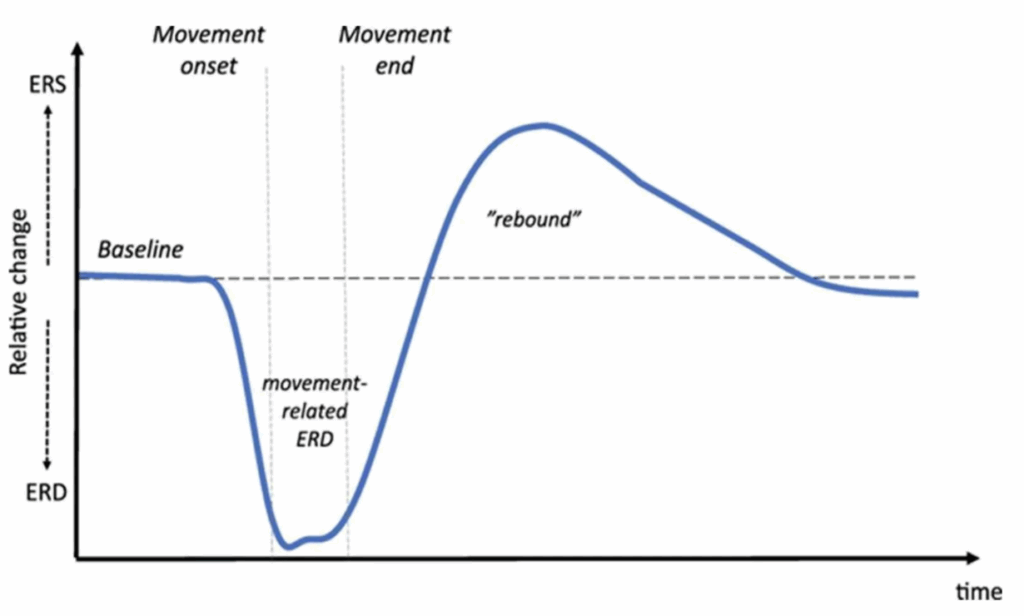
Process of Motor Imagery
Here is the correct sequence for a single, clean motor imagery trial:
- Baseline: both μ and β rhythms are at their resting, baseline power.
- Imagery Starts:
- Significant ERD in μ – Power drops sharply and significantly.
- ERD in β – simultaneous decrease in β power
- During Imagery: Both rhythms remain suppressed
- Imagery Stops:
- ERS in μ – gentle decrease in the power of μ rhythm, rebound is less significant
- Significant ERS in β – Has a very strong and clear rebound, known as the “beta rebound.”
- Post-Imagery: Less Significant ERS – There is a rebound, but it’s a gentle return to baseline. It typically does not overshoot into a strong, high-amplitude ERS like the β rhythm often does.
- Resettled: The power returns to the original baseline level, ready for the next command.
Data Gathering:
| Time (seconds) | Phase | What the BCI Records & The Brain’s Response |
|---|---|---|
| 0.0 – 2.0 | Rest / Baseline | Records the baseline brain activity. The mu/beta rhythms are at rest (synchronized). |
| 2.0 – 3.0 | Cue | The user prepares. The BCI notes the start of the trial and the label (e.g., “Left Hand”). |
| 3.0 – 7.0 | Imagery / Task | Records the key data. The BCI looks for ERD (power drop) in the mu/beta rhythms over the brain’s sensorimotor cortex. |
| 7.0 – 9.0 | Rest / Pause | The brain rhythms recover from ERD and often show a rebound (ERS). This pause prevents mental fatigue. |
Key Concept: Baseline is the resting state of the brain, ERD and ERS are all calculated relative to this baseline power.
Annotations: During data recording, the BCI software automatically inserts a digital marker, or in other words, an annotation, into the EEG data stream at the exact moment a specific event happens.
Epoching:
It is taking a long, continuous EEG recording and cutting it into many short segments called trials at predefined markers such as “left-cue.”