State Diagrams
State diagrams are used to abstract functions such as a controller, it consist of a set of states through which it sequences. The current state depends on the previous state combined with the previous values and the next state depends on the current state combined with the current values.
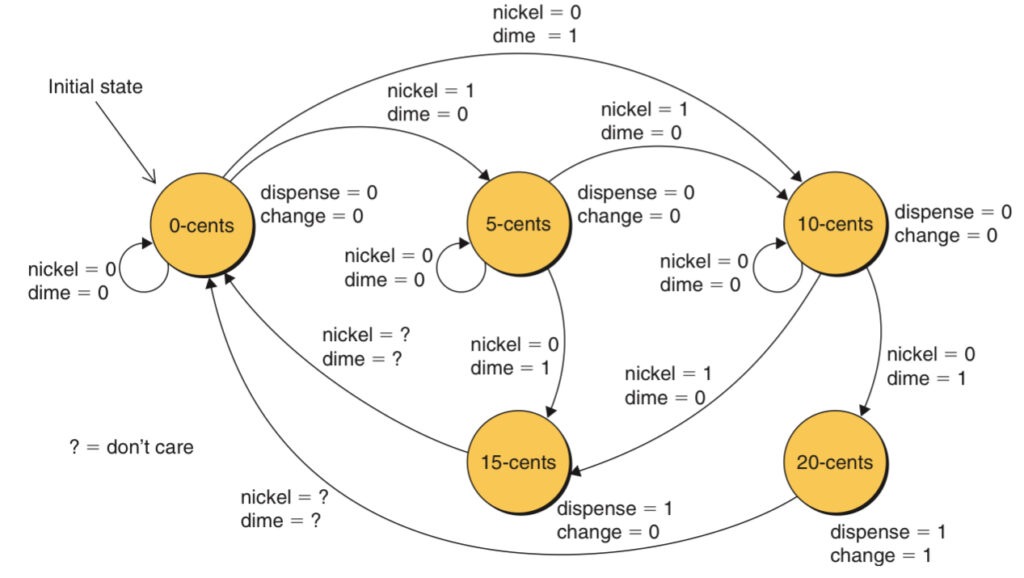
The arcs connecting the states are called state transitions and the values of the inputs associated with the state transitions are called guard conditions.
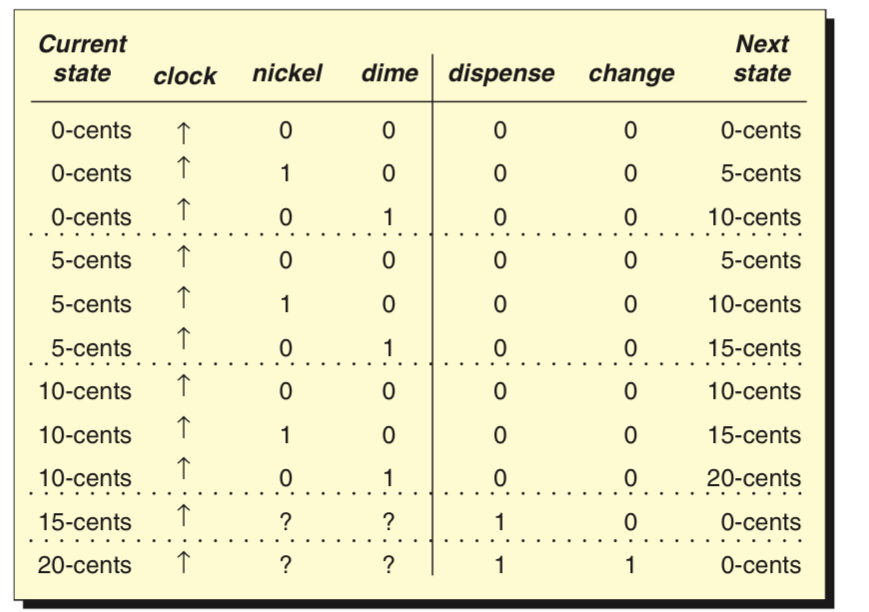
State Tables
A state table is another way of representing state diagrams. It is similar to a truth table but also includes the controller’s current state as an input and its next state as an output.
State Machines
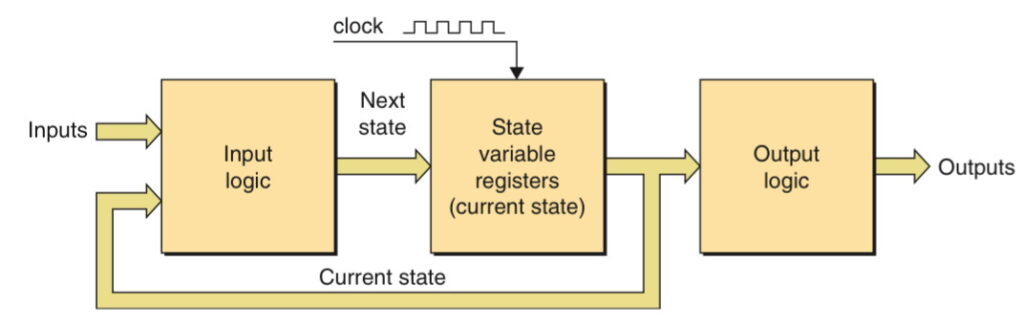
The actual implementation of a function such as the controller is called a state machine. There are two types of synchronous state machines, Moore and Mealy machines.
In a Moore machine, the outputs are derived only from the values in the state variables.
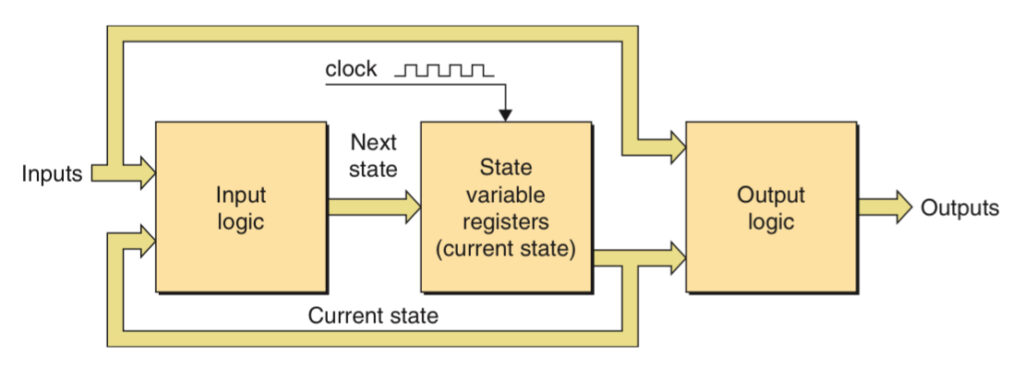
In a Mealy machine, the outputs may be derived from a combination of the values in the state variables and one or more of the inputs.
State Assignment
State assignment is the process by which the states are assigned to the binary patterns of logic 0s and 1s that are to be stored in the state variables. One common form of state assignment is binary encoding, 2 registers can be assigned four binary values, and three registers can be assigned eight binary values.
The actual process of binary encoding state assignment is a nontrivial problem when you choose 5 states from the 8, there are 6720 possible combinations. Each of these solutions may require a different arrangement of primitive gates to construct the input and output logic, which in turn affects the maximum frequency that can be used to drive the system clock.

A product term is a group of literals linked by & (AND) operators and a literal is any true or inverted variable.

One-Hot Encoding
One-hot encoding is another form of state assignment, in which each state is represented by an individual register. The one-hot technique typically requires a greater number of logic gates than binary encoding. However, the logic gates are used to implement simpler equations, so it results in faster state machines that can operate at a higher clock frequency.