Analogue-To-Digital
A transducer is a device that converts the input energy of one form into the output energy of another. An appropriate transducer that converts the detected analogue quantity to a suitable form is called a sensor.
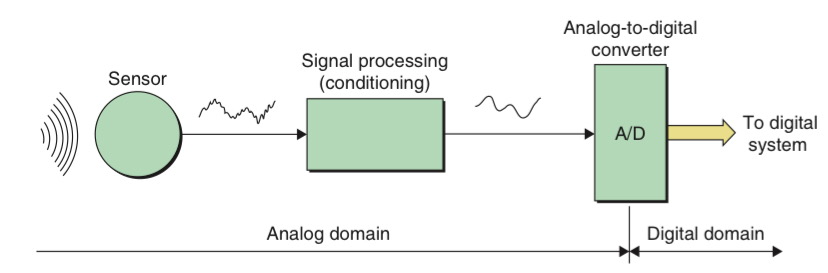
The output from the sensor may undergo some form of signal processing like filtering and amplification before being passed to the A/D converter and this signal is referred to as conditioning. The A/D converter accepts the conditioned analogue voltage and converts it into a series of equivalent digital values by sampling and quantization.
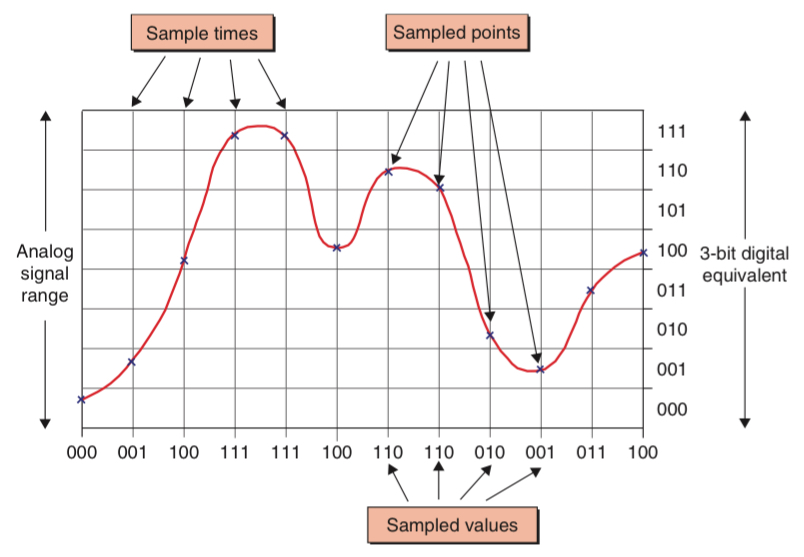
The analogue signal is divided into a set of discrete bands or quanta. At each sample time, the A/D converter determines which band the analogue signal falls into and outputs the equivalent binary code for that band. The concept of quantization noise or quantization error refers to the difference between the original real-world analogue signal and the quantized digital value caused by rounding or truncating the analogue signal to the nearest digital quanta.
Digital-To-Analogue
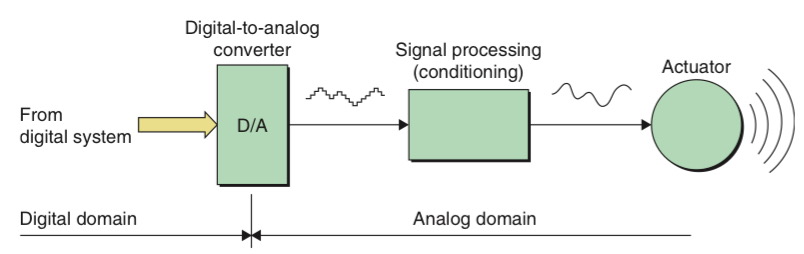
A D/A converter accepts a digital code and transforms it into a useful corresponding analogue current or voltage using an appropriate transducer called an actuator. The conversion occurs at regular time intervals and the output from the D/A converter undergoes some form of conditioning before being passed to the actuator.
Analogue Signal Processing (ASP)
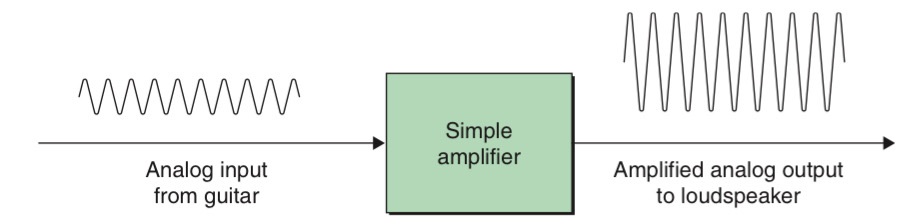
A simple form of Analogue Signal Processor is a basic analogue amplifier. For example, when we fed the signal into the input to the amplifier and use the amplified output to drive a loudspeaker.
A more complex form of analogue signal processing is to use a signal generator to output a sine wave and to use the amplitude of this sine wave to drive a voltage-controlled amplifier.
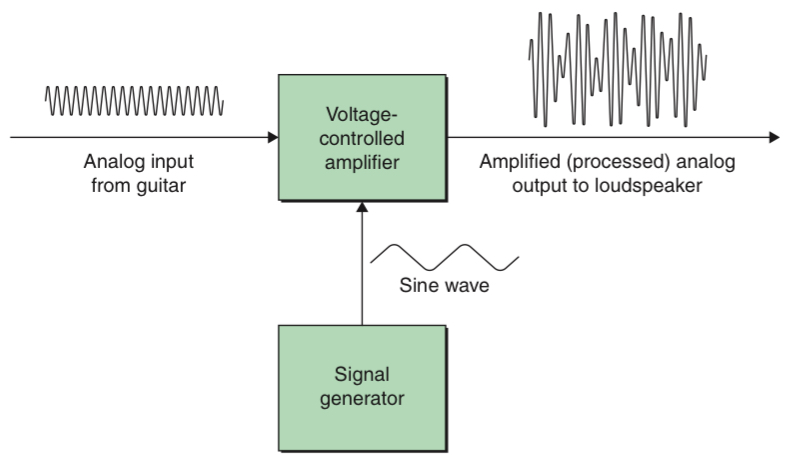
Analogue signal processing can be very effective but is limited to things like amplification, filtering, and signal conditioning.
Digital Signal Processing (DSP)
We can process digital values in the digital domain, and a lot more variety of signal processing algorithms can be applied to it to simulate for example reverb, delay, or distortion effects on the signal.